With medical technology rapidly evolving considerably, recently, we got to see some amazing inventions in the field of imaging. Clinical radiology is one such tool that has been a critical diagnostic tool to monitor and predict the result of the treatment provided. Even the enabled images are processed and easily transmitted all over the world with technological advances. The field of radiology has expanded, and the knowledge of this technology is used to train sub-specialty cases.
The improved clarity of the image processes in radiology has cut down the requirement of invasive tissue sampling and has discovered diseases of the pituitary gland to bone dysplasia and also conditions of the fetus, which are unseen through many tests. The future of clinical radiology has increased the range of diagnostic information to identify disease sites and morphology, and there is no evidence of a reduction in the pace.
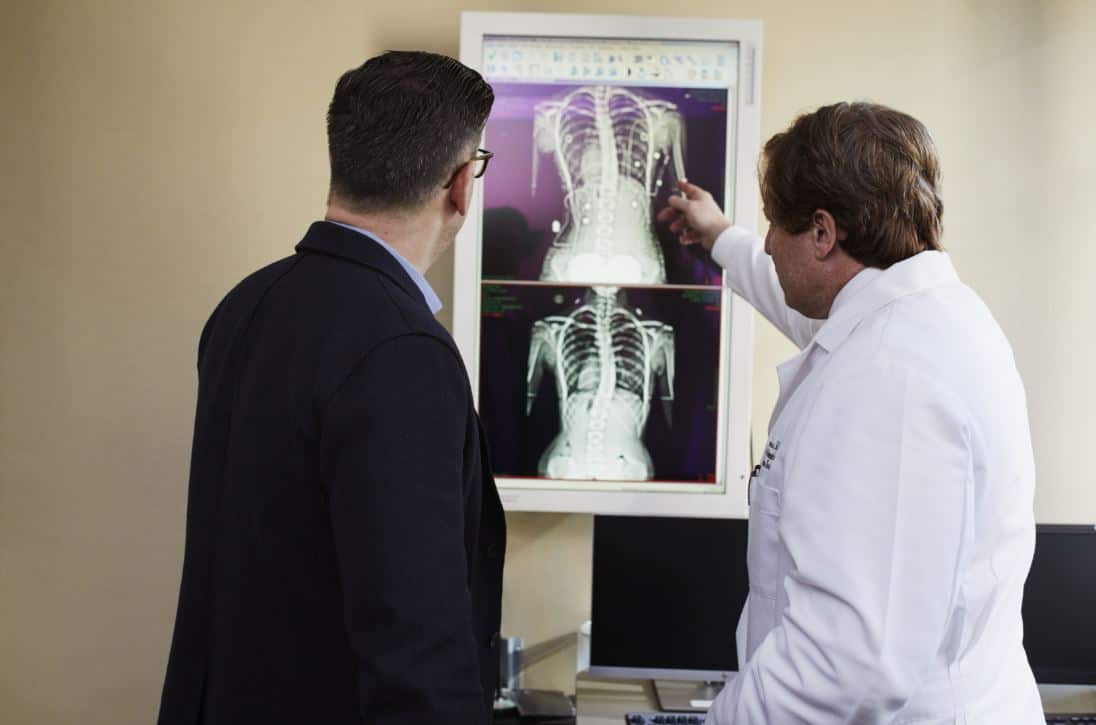
For diagnosing and treating extreme medical conditions, doctors require accurately detailed assessments. Clinical radiology is a diagnostic tool that plays a vital and swift role in detecting specific requirements of the patients. With the help of clinical radiology, one can discover the clinical history and anatomy of the patient. Radiologists use this specialized branch of medicine to capture pictures of the internal system of the body. This medical specialty uses state of the art equipment and a range of techniques to diagnose and treat diseases seen within the body.
Radiologists have to be proactive in the process of surviving the surrounding of this profession with foresight and flexibility. They need to use some of the latest imaging techniques in clinical radiology, which are commonly known as – X-ray, fluoroscopy, computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In hospitals, a range of radiological examinations is carried out by these imaging devices.
- For skeletal and soft tissue abnormalities, clinical radiology has vast diagnosis procedures.
- X-rays are useful to examine bones, teeth cavities, and foreign objects gathered in various parts of the body.
- Fluoroscopy can provide images of the digestive system.
- Angiography is used to investigate heart ailments and blood flow of blood vessels.
- Computed tomography gives all sectional views to identify and detect the diseases.
- Radioactive tracers examine the functions of the kidneys or heart.
- The ultrasound is used to detect pregnancy, gynecology problems, abdominal issues, and musculoskeletal conditions.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is done to get high-quality images of the interior of body parts.
Such benefits in the development of a clinical setting have given rise to faster imaging machines with less risk and at lower costs. One can rely on veteran firms to implement the best assets for healthcare services.
They have the core diagnostic imaging skills, with competence in technical interventions to provide proper care to the patients. Visit website considering the dynamics of clinical radiology and how one can achieve a better and more accurate diagnosis than ever before.
The other Interventional techniques carried by specialists in clinical radiology to diagnose a disease include:
- Esophageal stents are inserted into the esophagus to treat blockages of that area.
- Angioplasty is commonly used to remove blocked arteries of a heart patient by inserting a balloon or stent that allows blood to flow more freely.
- Angiography is a particular type of e-ray carried to diagnose the blockages of arteries and veins in the heart.
- Bile stent is inserted to allow bile drain from the liver.
Needle biopsy is pricked on a specific part to check if the tumor is benign or malignant.